Freedoms of the Air (freedom airlines) are a set of commercial
rights granting a country's airlines the privilege to enter and land in another
country's airspace. In other meaning, they are economic protocols agreed to by
countries for the commercial flow of revenue traffic by air.
The Chicago Convention stated that every country has complete and exclusive sovereignty over the airspace above its territory, and there is no recognition of the right of peaceful passage. That is why freedoms of the air have been introduced.
Note. I used the word " country" instead of "state".
Another reason, because of disagreements
over the extent of aviation liberalization in the Chicago Convention, triggered
by the United States' proposal of a standardized set of separate air rights to
be negotiated between countries. Most other countries were concerned that the
size of the United States airlines would dominate air travel if there were no
strict rules.
ICAO characterizes all "freedoms"
beyond the Fifth as " so-called" because only the first five
"freedoms" have been officially recognized as such by international
treaty. The use of the terms "freedom" and "right" confers
entitlement to operate international air services only within the scope of the
multilateral and bilateral treaties (air services agreements between countries).
We can say that the freedoms of the air are
the fundamental building blocks of the international commercial aviation route
network.
Freedoms of the Air
First Freedom of the Air
An overflight right or right of overflight
is the right or privilege, in respect of scheduled international air services,
granted by one country to another country or country to fly across its
territory without landing.
Second Freedom of the Air
A technical stop right or right of
technical stop is the right or privilege, in respect of scheduled international
air services, granted by one country to another country or country to land in
its territory for non-traffic purposes.
Third Freedom of The Air
The right or privilege, in respect of
scheduled international air services, granted by one country to another country
to put down, in the territory of the First Country, traffic coming from the home country of the
carrier.
Fourth Freedom of The Air
The right or privilege, in respect of
scheduled international air services, granted by one country to another country
to take on, in the territory of the First Country, traffic destined for the home country of
the carrier.
Fifth Freedom of The Air
The right or privilege, in respect of scheduled international air
services, granted by one country to another country to put down and to take on,
in the territory of the First Country, traffic coming from or destined to a
third country.
The so-called Sixth Freedom of the Air
The right or privilege, in respect of
scheduled international air services, of transporting, via the home country of
the carrier, traffic moving between two other Countries. The so-called Sixth
Freedom of the Air, unlike the first five freedoms, are not incorporated as
such into any widely recognized air service agreements such as the "Five
Freedoms Agreement".
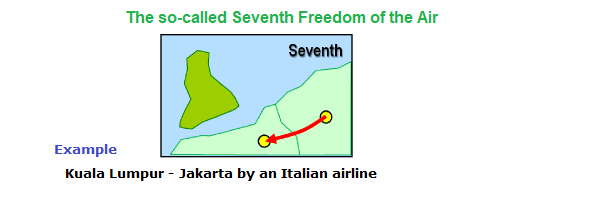
The so-called Seventh Freedom of the Air
The right or privilege, in respect of
scheduled international air services, granted by one country to another country,
of transporting traffic between the territory of the granting country and any
third country with no requirement to include on such operation any point in the
territory of the recipient country,
i.e the service need not connect to or be
an extension of any service to/from the home country of the carrier.
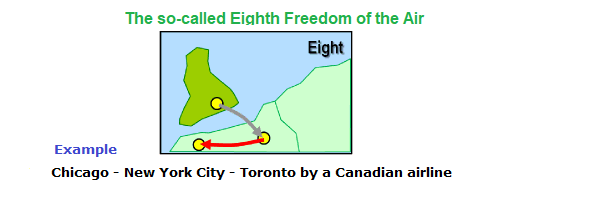
The so-called Eighth Freedom of the Air
The right or privilege, in respect of scheduled international air services, of transporting cabotage traffic between two points in the territory of the granting country on a service that originates or terminates in the home country of the foreign carrier or (in connection with the so-called Seventh Freedom of the Air) outside the territory of the granting country.
The so-called Ninth Freedom of the Air
The right or privilege of transporting
cabotage traffic of the granting Country on service performed entirely within
the territory of the granting country.